Ajax的作用
(1)不刷新页面更新网页
(2)在页面加载后从服务器请求数据
(3)在页面加载后从服务器接收数据
(4)在后台向服务器发送数据
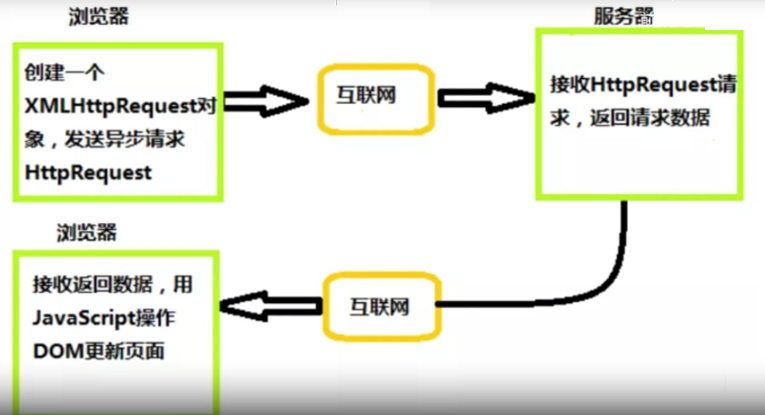
Ajax工作原理——XMLHttpRequest对象
(1)Ajax不是新的编程语言,而是一门提供网页局部刷新的技术。
Ajax最大的优点是在不重新加载整个页面的情况下,与服务器交换数据并更新部分网页内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
//封装一个ajax请求
function ajax(option) {
//创建XMLHttpRequest对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//初始化参数的内容
options = options || {};
options.type = (options.type || 'GET').toUpperCase();
options.dataType = options.dataType || 'json';
const params = options.data;
//发送请求
if (options.type === 'GET') {
xhr.open('GET', options.url + '?' + params, true);
xhr.send(null);
} else if (options.type === 'POST') {
xhr.open('POST', options.url, true);
xhr.send(params);
}
//接收请求
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
let status = xhr.status;
if (status >= 200 && status < 300) {
options.success && options.success(xhr.responseText, xhr.responseXML);
} else {
options.fail && options.fail(status);
}
}
}
}
|
(2)XMLHttpRequest对象在调用send()前需要调用哪个方法?答案是:open()
1
|
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
|
1
2
|
xhr.open('get', 'test.html', true);//与服务器建立连接
xhr.send();//需要什么内容,告诉服务器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('get', 'test.html', true);
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadyStateChange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
/**
* 0:请求还没有建立(open执行前)
* 1:请求建立了还没发送(执行了open)
* 2:请求正式发送(执行了send)
* 3:请求已受理,有部分数据可以用,但还没有处理完成
* 4:请求完全处理完成
*/
alert(xhr.responseText); //返回的数据
}
}
|
因此,可以看到.send()前是.open()
